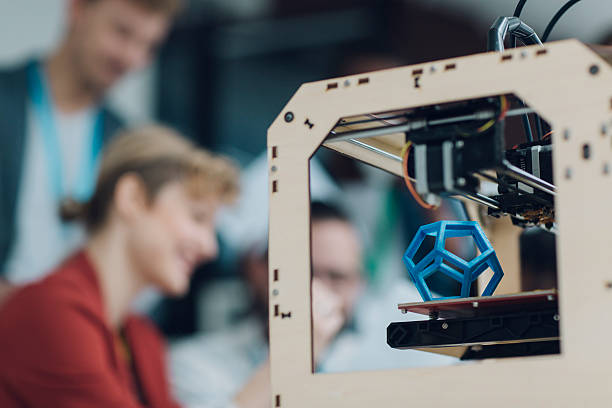
The advent of 3D printing technology has brought about a significant shift in manufacturing, design, and creativity worldwide, with Malaysia being no exception. Central to this revolution is 3D modelling, a process that enables the creation of digital blueprints for physical objects. 3D modeling for 3D printing Malaysia has emerged as a key driver of innovation, offering new opportunities for industries.
The Importance of 3D Modelling in Malaysia’s 3D Printing Landscape
3D modelling serves as the foundation for successful 3D printing projects. This section explores its critical role in transforming ideas into tangible products:
- Design Precision: 3D modelling allows for the creation of highly detailed and precise designs, essential for the accuracy and quality of 3D printed objects.
- Customization and Flexibility: It offers unparalleled flexibility in design, enabling customization that meets specific needs or creative visions.
- Efficiency and Cost Reduction: By allowing designers to identify and rectify issues before printing, 3D modelling reduces material waste and production costs.
Advancements in 3D Modeling Technologies in Malaysia
This section delves into the technological advancements and software innovations enhancing 3D modeling for 3D printing Malaysia:
- State-of-the-Art Software: Introduction to leading 3D modelling software used in Malaysia, including Blender, Autodesk Fusion 360, and SketchUp, highlighting their features and applications.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: How emerging technologies are streamlining the design process, improving accuracy, and reducing the time from concept to print.
Heading 3: Applications of 3D Modelling for 3D Printing Across Malaysian Industries
Healthcare
- Custom Medical Devices: Production of tailor-made prosthetics and dental implants that fit patients with unprecedented precision.
- Surgical Models: Creation of anatomical models for pre-surgical planning and educational purposes.
Architecture and Construction
- Architectural Models: Utilisation of 3D modelling for detailed architectural mockups, aiding in visualisation and planning.
- Construction Prototyping: Development of prototypes for components, reducing errors and streamlining the construction process.
Education
- Enhanced Learning Materials: Production of educational models that aid in teaching complex concepts in science, history, and mathematics.
- Research and Development: Facilitation of research projects with custom-made models and prototypes.
The Future of 3D Modeling and Printing in Malaysia
The concluding section outlines the potential future developments and challenges in the field of 3D modeling for 3D printing Malaysia:
- Growing Market Demand: With the increasing adoption of 3D printing across various sectors, the demand for skilled 3D modellers is on the rise.
- Challenges and Solutions: Discussion on the challenges faced by the industry, including the need for skilled professionals and the potential solutions through education and training programs.
- Innovation and Expansion: The potential for new applications and innovations in 3D modelling and printing, highlighting Malaysia’s position as a hub for technological advancement in Southeast Asia.
Conclusion
3D modeling for 3D printing Malaysia represents a significant leap forward in Malaysia’s quest for innovation and technological advancement. By bridging the gap between digital designs and physical reality, it opens up a world of possibilities for customization, efficiency, and creativity across diverse industries. As Malaysia continues to embrace and invest in these technologies, the future of 3D modelling and printing looks promising, with the potential to reshape the country’s industrial landscape and beyond.